Source: outlookindia.com
To mark the seventh anniversary of Nirbhaya gang rape, the Bihar Police has announced a district-wide programme to prevent violence against women and girls.
December 16, 2019 was the seventh anniversary of the gut-wrenching rape and murder of 23-year-old Nirbhaya, the brutality of which still sends chills down our spines. The outrage that followed the gruesome incident compelled the government to recognise the magnitude of the problem and form a committee to look into reforming anti-rape law. A slew of recommendations was also made for prevention of violence against women and children, one of which was to augment the police force by investing in community policing.
To this end, the Bihar Police started a community initiative in 2016 to collaborate with women and girls in 32 police stations in Patna and 20 police stations in Gaya to prevent violence, abuse, and exploitation. The initiative has already yielded benefits as it has instilled a greater confidence in communities that the Police will partner with them to keep them safe.
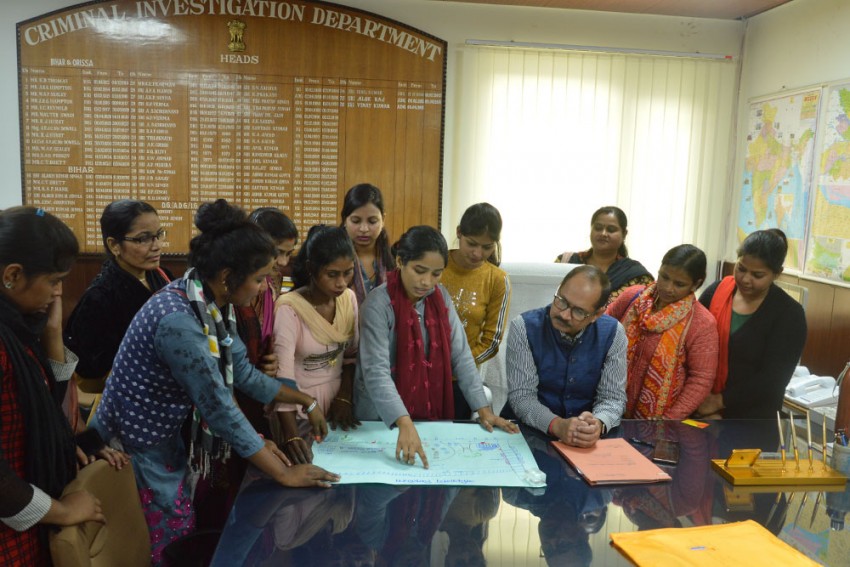
To mark the seventh anniversary of Nirbhaya gang rape, the Bihar Police has announced a district-wide programme to prevent violence against women and girls. Assistant Director General Vinay Kumar of the Criminal Investigation Department said, “All the police stations across Patna districts will have ‘Women and Girl Safety Panels’ trained by Mumbai-based NGO Aangan Trust. The groups, comprised of women and children from all the police stations in the district, will actively engage with Bihar Police to identify and address threats to the safety of women and children in the region.” These monthly meetings comprise a significant investment in community policing and using local, real-time data from the ground to inform stronger policing in Patna.
Each chowki (police post) will have designated police personnel specialized to deal with cases of violence against women and children and shall be approachable to the community at all times. Police officials will initiate community meetings along with women volunteers to disseminate information on safety and legal mechanisms. Through regular meetings with the safety groups, the Police will leverage this mechanism to identify cases of child harm across the districts, work with community to co-create solutions to threats to child safety and take meaningful action in preventing harm.
Strengthening community policing systems has been shown to have positive effects on the police’s perception and efficacy, according to the Task Force on 21st Century Policing led by former U.S. President Barack Obama. In particular, trust and legitimacy are indicators that are shown to improve through increased interface with the community, and both of these factors have an impact on the police’s ability to do its job to protect the community. “Change begins with listening,” reads the first section of the 21st Century Policing Handbook. It is with this intention that the Bihar Police has set out to meaningfully engage with community members around child safety.
In 32 police stations of Patna, there are already active groups who engage with the police monthly. Police in these police stations have conducted activities like open houses, meet with adolescent girls who have mapped risks, increased patrolling, or carried out school safety campaigns.
Headquarters Inspector General Mr. Nayyar Khan said of the collaboration, “To tackle the grave issue of gender-based violence, it is crucial to incorporate the valuable perspectives of women and girls. Bihar Police has been collaborating with Aangan Trust to bring police and community together since 2016, and we look forward to continuing this engagement.”
As a result of local community data shared with the Bihar Police by women and girls, the police has taken actions such as increasing patrolling on unsafe routes, spreading awareness of legal systems protecting women and children against violence, conducting school safety campaigns, and organising regular community meetings to have a better understanding of risks at the grassroots level.